small useful git tricks
Here’s a couple of git aliases I use all the time. It gives you a quick and clear overview of your branches and
commits. It can even watch for changes in realtime and show you any changes.
A better git log
Add this to your .gitconfig:
| |
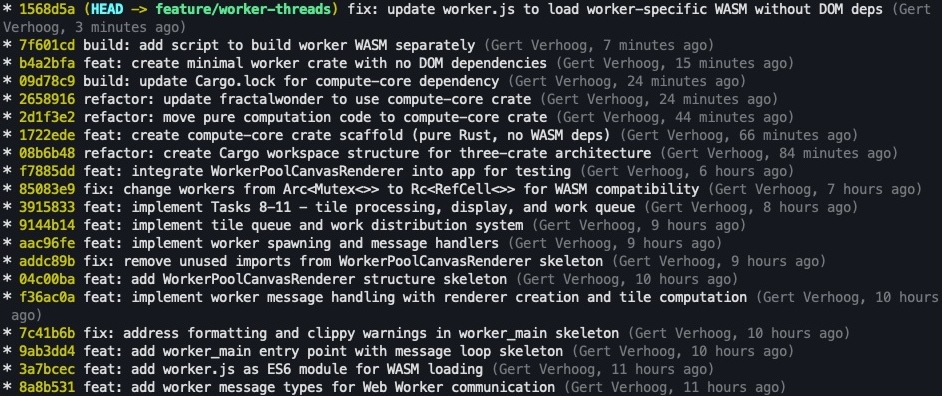
Run git tree and you get a compact view of your commit history with branches, colored hashes, commit messages, and authors. The --all flag shows all branches, not just the current one.
Live-updating git log
This one needs viddy, which is like watch but better. Install it with brew install viddy on Mac or go install github.com/sachaos/viddy@latest if you have Go.
| |
Run git watch-tree and you get a live view that updates every second. The head -n $(tput lines) part limits the output to your terminal height so it doesn’t scroll. The -c color.ui=always keeps the colors when piping through viddy.
I keep this running in a terminal while I work. When I commit or switch branches, the view updates automatically.
Update: now shows files modified/untracked
Just add this to your ~.gitconfig alias section:
| |
What this does
The alias wraps two git commands in viddy, which re-runs them every second and highlights what changed:
| |
First it runs git status --porcelain through an awk script that counts untracked, modified, and staged files:
| |
The porcelain format is just ?? for untracked, .M for modified, M. for staged. Count them up, print a summary.
Then it runs your tree alias and limits the output to your terminal height:
| |
The -c color.ui=always keeps colors when piping through viddy.